The Importance of Game-Based Learning in Today’s Classroom
A modern education system uses technology to transmit education. The growing usage of digital games and applied sciences into learning environments has affected both the teaching of educators and the learning of students. Game-Based Learning (GBL) can be successfully used to improve both learning and teaching. VR Quest® is an educational application that introduces 3D Game Design and Immersive Virtual Reality technology into the classroom. It’s mission is to enrich students’ lives by offering computer instruction in VR game design while teaching standards-based lessons in social studies. Below is research that shows the importance of using games in instruction.
On Games
Because digital games have the potential to transform K-12 education as we know it, according to many . Certain varieties of digital games offer complex worlds in which individuals can playfully explore and experiment, repeatedly fail, and ultimately succeed. To navigate these immersive environments, players need to think critically and make meaningful choices.
Most American children are already familiar (if not obsessed) with digital games, and voluntarily spend the time it takes to up one’s performance. By aligning curricular objectives for STEAM, digital games have the potential to disrupt, modernize, and improve K-12 teaching and learning.
Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS), which emphasize the use of digital tools and systems to promote deeper learning and assess student progress are widely more prevalent in schools. Teachers are seeking ways to cover the new standards, and digital games offer a particularly appealing option.
Who’s Using Games in the Classroom?
In a survey on K-8 teachers, more than four out of five teachers (82%) indicated that they play computer or video games, smart phone game apps, and/or social media games – including 62% play at least weekly, and 27% play every day.
All teachers need adequate training on how to integrate digital games into their teaching, even if they are digital natives or even self-proclaimed gamers. VR Quest comes with training partners, as well as information online.
On Immersive Games
Highly immersive, highly complex, and highly engaging experiences afforded by certain types of video games don’t just improve learning, they can improve the kind of learning that children need to do well in school and life beyond.
1. Gee, 2003a; Gershenfeld, 2014; Prensky, 2001; Shaffer, Squire, Halverson, & Gee, 2005
2. Shute, 2011; Tucker, Tucker, & Smith, in press
3. Becker, 2007; Mishra & Koehler, 2006
4. Lei, 2009

Social Awareness
The ability to take the perspective of and empathize with others, including those from diverse backgrounds and cultures. The ability to understand social and ethical norms for behavior.
- Perspective-taking
- Empathy
- Appreciating diversity
- Respect for others

Relationship Skills
The ability to communicate clearly, listen well, cooperate with others, resist inappropriate social pressure, negotiate conflict constructively, and seek and offer help when needed.
- Communication
- Social engagement
- Relationship-building
- Teamwork

Responsible Decision-Making
The realistic evaluation of consequences of various actions, and a consideration of the well-being of oneself and others.
- Identifying problems
- Analyzing situations
- Solving problems
- Evaluating
- Reflecting
- Ethical responsibility

Self-Awareness
The ability to accurately recognize one’s own emotions, thoughts, and values and how they influence behavior. The ability to accurately assess one’s strengths and limitations, with a well-grounded sense of confidence, optimism, and a “growth mindset.”
- Identifying emotions
- Accurate self-perception
- Recognizing strengths
- Self-confidence
- Self-efficacy
Self-Management
The ability to successfully regulate one’s emotions, thoughts, and behaviors in different situations — effectively managing stress, controlling impulses, and motivating oneself. The ability to set and work toward personal and academic goals.
- Impulse control
- Stress management
- Self-discipline
- Self-motivation
- Goal-setting
- Organizational skills
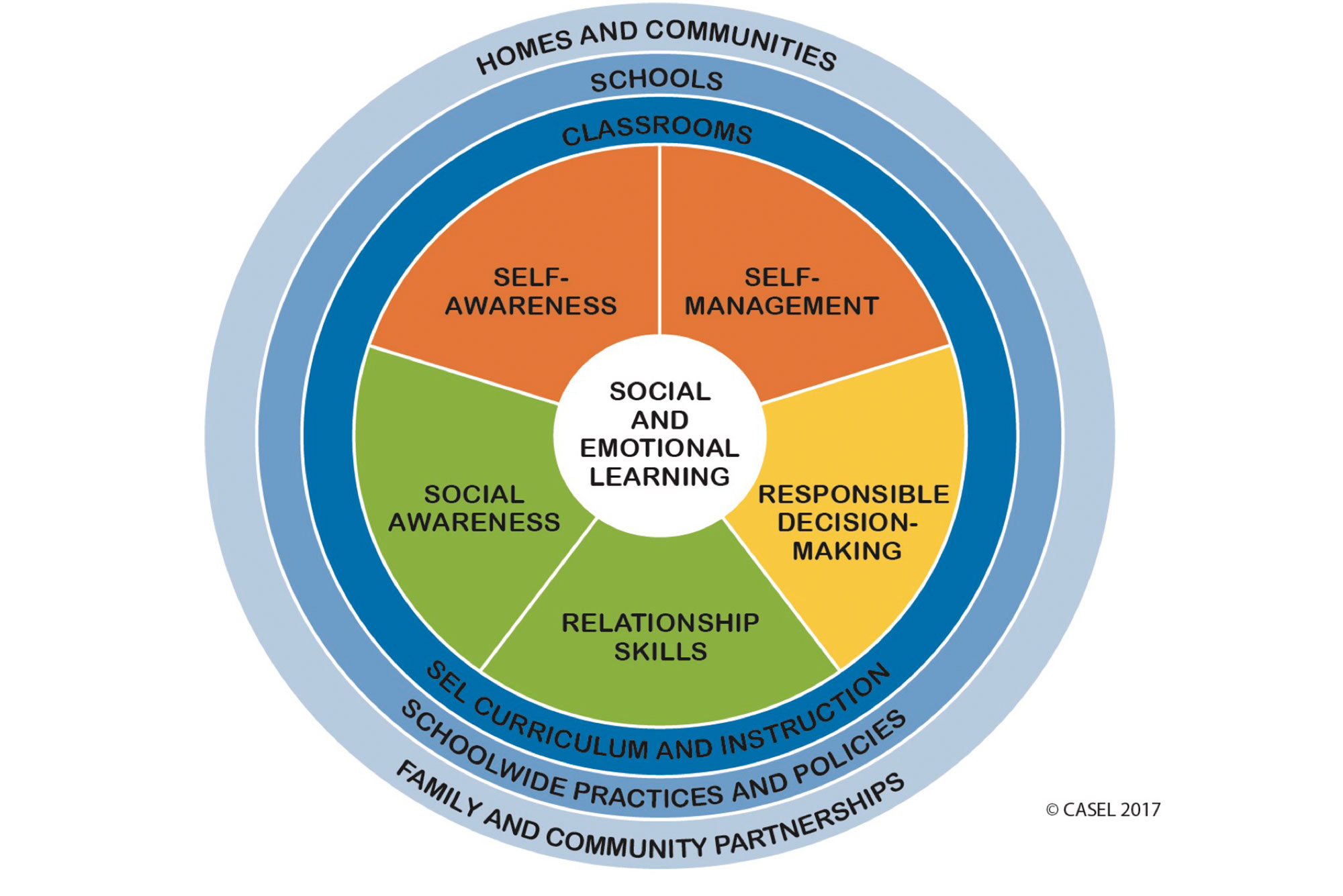
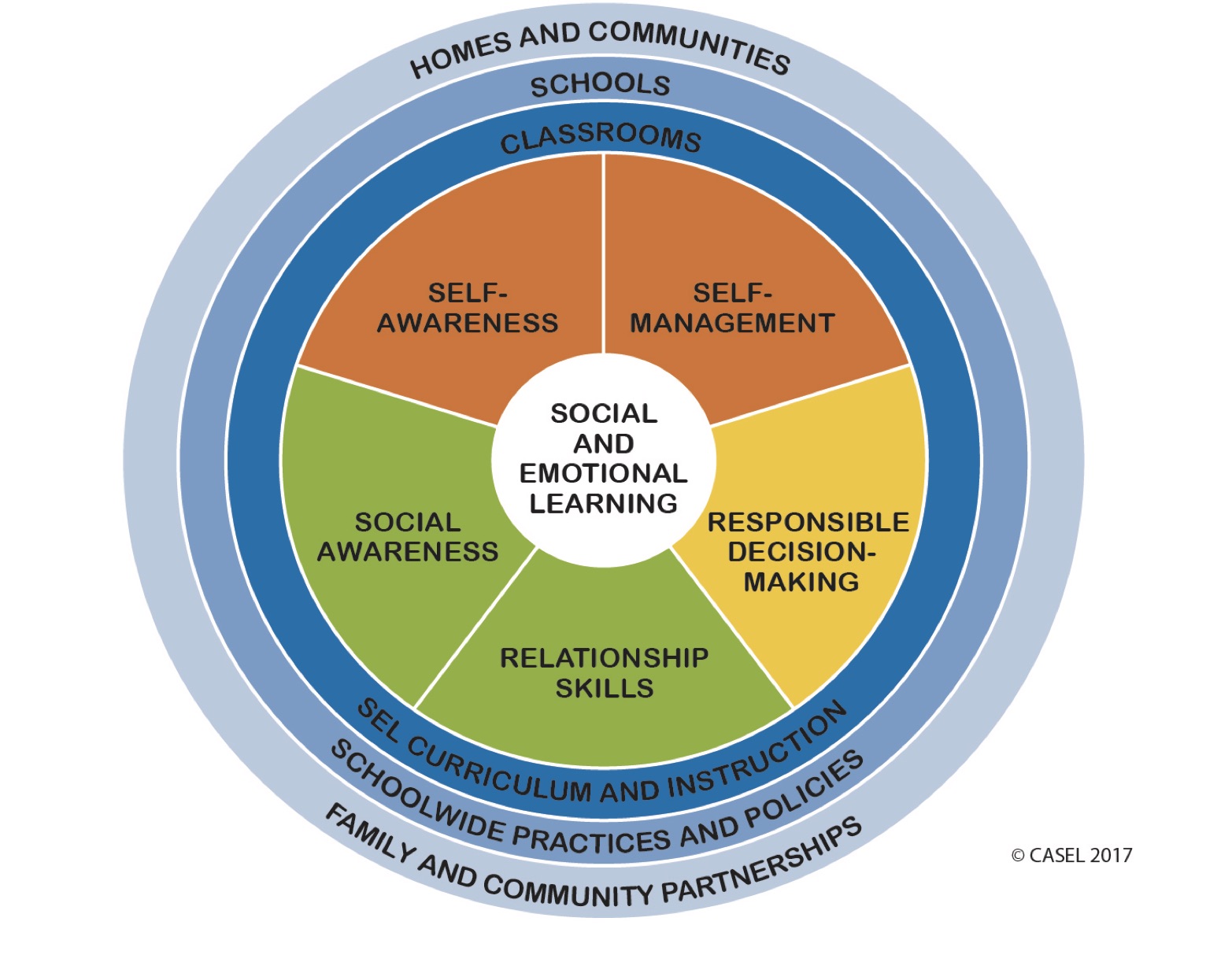
CASEL’s Framework
Identifies Five Core Competencies:
- Self-awareness
- Self-management
- Social awareness
- Relationship skills
- Responsible decision-making
According to research conducted by Penn State, “Social and Emotional Learning protects against adverse risk-taking behaviors, emotional distress, and conduct problems, and contributes to health, academic achievement, and success later in life” (Penn State University). In utilizing VR Quest®, scholars unconsciously draw upon Social and Emotional Learning components, commonly referred to as SEL. The VR Quest® creation process requires scholars to embed the virtual experience with content knowledge. In doing such, participants develop the dispositions needed to better manage emotions as they begin to feel a strong sense of compassion and empathy for others’ lives and experiences. Further the process of creating more equitable outcomes and learning environments greatly contributes to scholars’ social and emotional development.
The CASEL 2017 model, above, indicates five competencies necessary for meeting interpersonal, life and school-based success. As VR Quest® users build their games, they become better equipped in the first component or domain, Self-Awareness. For example, in the Underground Railroad VR Quest®, scholars become more in tune with their emotions and their values through building. As they gather research and recreate true events, a strong sense of right and wrong becomes more prominent. Scholars better understand each person has a voice, as a citizen and must utilize it and to speak up against evil and atrocities committed by mankind onto others. When children recognize how thoughts, feeling and actions are interwoven, they are becoming more cognitive, thinking deeply and at a higher level of self-awareness.
The Self-Management Domain is primarily evidenced when scholars have dispositions giving them the ability to control emotions and behaviors. Specifically, this pertains to skills that facilitate goal setting, persevering through challenges, managing stress and impulse control. This is best displayed in the setting of timelines for the various objectives of the game’s completion, persisting through the failure points during game creation and delaying the outcome of the game versus immediate gratification in delivering the justice, or end line.
The Social Awareness Domain is a natural progression as scholars quickly understand the perspective of diverse people from different cultures and backgrounds. It is through the game building process that this basic comprehension and ability to live others’ experiences so to speak helps scholars develop a stronger sense of compassion and empathy. This domain is all encompassing as children foster a better understanding of social norms and standards and see their support systems and resources within the community, school and home life.
The fourth domain, Relationship Skills, involves the ability to actively listen, articulate clearly, collaborate and seek assistance when needed, constructively negotiate conflict and resist social pressures. VR Quest® promote relationships skills as scholars collaborate during the game building process. Acting in units or as a team, scholars use social skills and interdependent dispositions necessary to establish healthy, balanced and fulfilling relationships.
Lastly, competence in the Responsible Decision-Making Domain fosters reflection, being able to determine realistic evaluation of different actions and their consequences and implementing ethical standards. VR Quest® promotes social emotional learning in this domain when scholars apply ethical concepts and insert artifacts that demonstrate their analysis of past historical wrongs. As new generations of future leaders are being groomed in public schools every day, the ability to instill dispositions that are compassionate and demonstrate empathy are now more vital than ever before.
In conclusion, the National Equity Project states that every teacher has the ability to foster educational equity through relationship building and promoting social and emotional development. VR Quest® provides rigorous instruction encompassed within a supportive environment that builds trust and rapport in a collaborative setting. Scholars are guiding and directing their own instruction with personalized and meaningful creation of content. Through this creation process, factual information is not only retained and internalized more thoroughly, but scholars begin to reflect and demonstrate higher order critical thinking skills without prompting from adults. VR Quest® assists in developing a positive school culture supporting academic achievement through a combination of content knowledge and technological creation skills. Thus, scholars are equipped with dispositions needed to ensure they are productive and responsible citizens and community members. By fostering a culturally responsive virtual world that translates over into real life dispositions and classroom culture, VR Quest® creation helps “affirm racial, and cultural identities; prepare students for rigor and independent learning; develop students’ abilities to connect across lines of difference; elevate historically marginalized voices; and empower students as agents of social change ” (NYSED). Every scholar has very different needs and brings different background knowledge to the classroom. Through the hands on and collaborative process reinforced in a trusting environment, VR Quest® enables instruction to become more personalized and differentiated. This is especially significant in differentiating instruction for high-need scholars, multiple language learners, at-risk children and others requiring greater rigor and challenges. VR Quest’s® essence is structured around social and emotional learning and creation. The game creation process purposefully focuses on the skills and dispositions necessary for a collaborative and better future through all five competency domains. By helping to sharpen and improve equity, scholars’ choices and voice, ultimately there will be greater student agency that will improve the leadership in the U.S. for years to come.